Biometric ATM Iris Recognition: A Comprehensive Overview

Abstract
Human identity recognition is one of the key methods of authentication where their biometrics are used as identifiers such as the iris which is one of the most unique and stable biometric in humans. Therefore, ATM iris biometric recognition is a technology that uses the patterns of the irises of the eyes to identify and authenticate users to access their bank ATM accounts. This paper provides a comprehensive overview of biometric ATM recognition, covering its method of operation, current status, application use cases, advantages, disadvantages, and future prospects. The paper argues that biometric ATM iris recognition can enhance the security while providing convenience to banking, but also acknowledges that there are some limitations, and it poses some challenges that need to be addressed. Furthermore, there is contention that biometric ATM iris recognition will be the future of ATM authentication, if the issues of ethics and privacy, scalability and maintenance, acceptance, and trust, and most importantly the cost are mitigated.
Introduction and definitions
Human identity recognition is one of the key methods of ensuring authorized information access to individuals, where their biometrics are used as identifiers [1]. According to Alwahaishi and Zdrálek [2], biometric identification is the process of verifying an existent's identity based on their physiological and/or behavioral characteristics. On humans these characteristics include fingerprints, face, voice, palm veins, and the iris. However, among them, the iris is one of the most distinctive and stable biometric, with a very low probability of false matches. This is evidenced by the Electronic Privacy Information Center [3] which found out that iris recognition false rate was 1 in 1.2 million compared to others like fingerprint, that had false rate of about 1 in 100,000.
The iris is the ring of tissue that surrounds the pupil of the eye with random patterns formed during the embryonic development and remain unchanged throughout the lifespan, except for some minor variations due to external factors like aging, diseases, or injuries [4]. Therefore, Iris recognition is a form of biometric identification that depend on the assumption that no two individuals have identical iris patterns, and that these patterns are stable and consistent over time; where pattern recognition techniques are used to analyse and identify an individual.
As explained by Wildes [5], biometric ATM iris recognition is where iris recognition technology is applied to automated teller machines (ATMs), where users can access their bank accounts and perform financial transactions by scanning their irises, without the need of other authentication methods like cards and PIN codes.
It is considered as a promising technology that can enhance not only the security but also the convenience of banking and provide an extra layer of security for banking applications that my require high-security access control.
Despite the possible challenges that biometric ATM iris recognition may pose, this paper argues to a position that biometric ATM iris recognition can improve the security while providing convenience of banking with a careful consideration and regulation. The paper explores the method of operation, a comprehensive overview of the current status, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and future prospects.
The current status of biometric ATM iris recognition
Biometric ATM iris recognition is still in its early stages of development and adoption with active exploration and experimentation. Several fintech, cyber security researchers and leading financial institutions have conducted pilot programs and trials to assess the feasibility and efficacy by integrating biometric ATM iris recognition into their existing systems and research innovations.
Notable Implementations
- Citibank (2015): Tested first biometric iris recognition ATM, allowing customers to withdraw cash using their irises. The ATMs reduced transaction processing time to about 10 seconds.
- Bank of America (2018): Experimented with iris recognition biometric ATMs, enabling card-free and PIN-free account access.
It is noteworthy that there is limited literature and statistics on the current adoption of biometric ATM iris recognition; however, [8] indicate that, as of 2022, there was over 1000 ATMs in Montreal and Chicago that used iris recognition to authenticate users.
Current Research and Development
- Use of machine learning for fast and precise identification of irises [9]
- Development of contactless and mobile iris recognition systems [10]
- Improvement of iris image quality, normalisation and segmentation algorithms [11]
Operation of biometric ATM iris recognition
At a high level of abstraction, biometric ATM iris recognition primarily involves two phases: the enrolment and recognition. At enrolment, a trained person captures a picture of the user's iris, storing it within the ATM authentication database, usually during initial registration or user data updates. The acquisition stage involves users scanning their own iris and the system comparing it with the stored template to verify their identity.
Recognition Process Steps
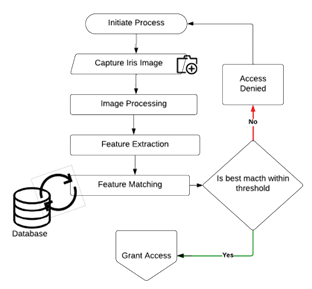
- Image Acquisition: The user's iris is captured using near-infrared
- Image Processing: Segmentation of the iris region, noise removal, and normalization
- Feature Extraction: Encoding into a compact feature vector using algorithms like Gabor filters
- Feature Matching: Comparing the feature vector with stored templates using metrics like Hamming distance
Applications cases of biometric ATM iris recognition
The primary application of biometric ATM iris recognition is to give a convenient but secure means of user authentication for banking transactions. Biometric ATM iris recognition can also be integrated with other biometric modalities, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to add another layer of authentication thus enhanced security as it can reduce the chances of false rate to almost zero [13].
Besides banking, biometric iris recognition have been applied to other contexts that require high-security access control with similar mode of operation, such as: government facilities (military bases, airports, border checkpoints), where iris recognition is used to verify the identity and clearance of personnel and visitors; has also been increasingly integrated into securing personal devices, properties, and information. Such as users can unlock their smartphones or access their premises such as an office by having their irises scanned.
Advantages of biometric ATM iris recognition
Compared to other methods of ATM user identification, such as PIN codes and cards, biometric ATM iris recognition has several advantages that make it more secure but also reliable, and convenient.
As evident in [3], the iris is one of the most unique and stable biometric traits, with a very low chance of false matches (error rate less than 0.01%) which implies ability of a high level of confidence and trust in the identity of the users, and prevention of fraud.
- Impossible to replicate compared to fingerprints and faces
- Can be scanned without physical contact
- Clean and potential control measure for disease spread
Disadvantages of biometric ATM iris recognition
Despite the high degree of accuracy and convenience, biometric ATM iris recognition has some limitations and challenges that are still limiting its adoption, which span through the privacy issues, external factors, and to the cost of implementation.
Major Limitations
- Requires substantial investment in setup and infrastructure
- Privacy concerns regarding collection and storage of biometric data
- Potential interference from external factors:
- Physiological: aging, diseases
- Environmental: lighting, reflections
- Behavioral: blinking, glasses, contact lenses
The future projection of biometric ATM iris recognition
With the extreme high levels of accuracy and convenience provided by biometric ATM recognition, and the pushing force from increased demand of fast, convenient but secure banking services in the current pursuit of modernisation, biometric ATM iris recognition is expected to experience extensive incorporation into banking systems, potentially becoming the future of ATM security.
Additionally, with the current fast rates of technology advancements and research in hardware design, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence, it is very likely to make it more cost-effective hence higher adoption.
Furthermore, biometric ATM iris recognition is likely to expand its adoption beyond banking, to other areas like smart cities and transportation, integration with other smart devices and systems, data security and privacy access controls.
In conclusion, with no doubt, biometric ATM iris recognition will be the future of ATM authentication, by capitalising on the strength, and leverage the research and technology to mitigate the issues of ethics and privacy, scalability and maintenance, acceptance, and trust, and most importantly the cost of setup.
References
- Gavrilova, M., Luchak, I., Sudhakar, T. and Tumpa, S. N. Artificial Intelligence in Biometrics: Uncovering Intricacies of Human Body and Mind. Springer, City, 2022.
- Electronic Privacy Information Center. Biometric Comparison Guide. Electronic Privacy Information Center (EPIC).
- Daugman, J. How iris recognition works. Elsevier, City, 2009.
- Wildes, R. P. Iris recognition: an emerging biometric technology. Proceedings of the IEEE, 85, 9 (1997), 1348-1363.
- Citigroup Testing Eye-Scanning ATM: No Bank Card Required. NBC News (2015).
- Lee and Justin Bank of America exploring use of iris recognition technologies. www.biometricupdate.com (2017).
- Simon, J., Kumar, U. S., Aarthi Elaveini, M., Vengaloor, R. P. and Phani Kumar, P. ATM Security Using Iris Recognition. Springer Nature Singapore, City, 2022.
- Premraja, D., K, C. D. S., K, A., S, M. and S, V. N. Iris based ATM Transaction using Machine Learning. City, 2023.
- Benalcazar, D. P., Tapia, J. E., Vasquez, M., Causa, L., Droguett, E. L. and Busch, C. Toward an Efficient Iris Recognition System on Embedded Devices. IEEE Access, 11 (2023), 133577-133590.
- Farouk, R. H., Mohsen, H. and El-Latif, Y. M. A. Iris Recognition System Techniques: A Literature Survey and Comparative Study. City, 2022.
- Polash, P. P. and Monwar, M. M. Human iris recognition for biometric identification. City, 2007.
- Thakkar, D. An Overview of Biometric Iris Recognition Technology and Its Application Areas. Bayometric (2016).