Exploring The Applications, Merits & Demerits, And Future Prospects Of Hadoop
Contents
Introduction
In today's era of social media, web traffic and business transactions that are extensive, massive volumes of data are generated at a variety, and high velocity often referred to as big data. To support informed decision making, data should be processed, however big data poses challenges for traditional data management systems, and to address these challenges, new frameworks are needed to store, process, and analyse big data efficiently and effectively.
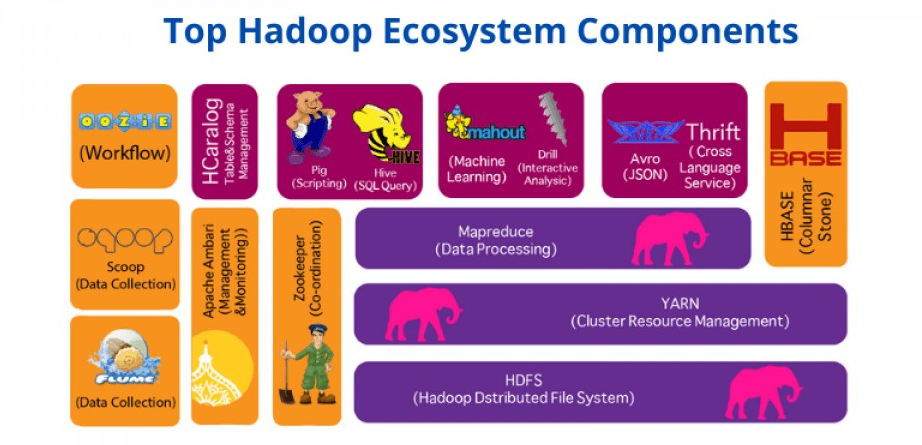
One of the most prominent and widely used frameworks for big data processing is Hadoop, which is an open-source framework. Hadoop was inspired by Google's MapReduce and Google File System papers, which proposed handling large data processes using clusters [1]. Hadoop consists of two main components: Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Hadoop MapReduce. HDFS is a distributed file system that provides high-throughput access to data across multiple nodes in a cluster. MapReduce is a programming model that allows users to write parallel applications that process data in key-value pairs [3].
Hadoop's core components: HDFS and MapReduce
Also, for extended functionality, Hadoop supports a variety of component extensions like Hadoop YARN, Apache Pig, Apache Hive, Apache HBase, Apache Spark, and many more.
Hadoop has been widely adopted by many organizations in various domains including Facebook, Amazon, Netflix, and IBM. Hadoop has also been used for scientific and academic research like genomics. However, as any other technology, Hadoop is not without limitations and drawbacks which include security, interoperability, fault tolerance, and scalability. In this writeup, the applications of Hadoop are explored, the advantages and disadvantages discussed and also the future prospects too.
Applications of Hadoop
Hadoop has been applied to various domains that require big data processing and analytics. This section discusses some of the applications of Hadoop:
E-commerce
Hadoop is widely used in the e-commerce industry where companies like Amazon, leverage Hadoop's ability to store and process large amounts of transactional, behavioural, and product data. Hadoop facilitates the fast processing of large data generated enabling product recommendation, customer segmentation, fraud detection, price optimization, and inventory management. For example, Amazon uses Hadoop to analyse customer reviews, ratings, and feedback to provide personalized recommendations [4].
Web Search
Web search engines, such as Google and Bing, need to index, and rank billions of web pages and provide relevant results to the user in a very short time. With Hadoop, web search engines can store and process massive amounts of web data using distributed and parallel computing. Google uses MapReduce to perform tasks like computing page ranks and generating snippets [1]. Bing also uses Hadoop to analyse user behaviour and optimize search quality [5].
Social Media
Social media platforms, such as Facebook, and LinkedIn, generate and collect huge volumes of user-generated data which require fast analysis like personalization, recommendation, sentiment analysis, trend detection, and advertising. Facebook uses Hadoop to store over 300 petabytes of user data and perform daily analytics [6]. LinkedIn uses Hadoop to power its skills and endorsements functionality.
The other fields where Hadoop has been used include healthcare where Hadoop is used to store and process large and complex medical data, such as electronic health records, genomic sequences, and sensor data; the education where schools store and process large amounts of data including student records, course materials, assessments, and feedback.
Advantages of Hadoop
Some of the advantages of Hadoop include:
- Scalability: Hadoop supports ease of adding or removing nodes from a cluster without affecting the performance and availability of the system hence a highly scalable framework that can handle data growth and complexity;
- Cost-effectiveness: From the fact that Hadoop is an open-source framework that uses commodity hardware for storage and processing, it is less costly than acquiring and maintaining expensive and specialized hardware and software;
- Flexibility: Hadoop is a flexible framework in that, it can handle various types of data, it can support various sources of data, and it can run various applications on top of its core components of HDFS and MapReduce;
- Fault-tolerance: as its mechanism of operation, Hadoop duplicates data blocks across multiple nodes in a cluster to ensure data availability and can automatically detect and recover from node failures and task failures hence preventing data losses [2, 4, 7].
Disadvantages of Hadoop
Despite its strength, Hadoop has some disadvantages. Hereafter are some of the major ones:
- Hadoop is primarily designed to handle large files, therefore, files that are smaller than the size of a Hadoop data block (128 MB) cause more disk seeks and network transfers hence reducing the efficiency and performance of the system;
- Hadoop relatively lacks adequate security and privacy features since these mechanisms are not provided by default implying that users rely on third party tools;
- to configure a Hadoop setup, it requires a steep learning curve and technical expertise with a good understanding of the underlying architecture, components, and concepts;
- given that it's based on batch processing, Hadoop is not suitable for real-time processing. Which leaves Hadoop users to use other frameworks like Apache Spark [2, 4, 7, 8].
Future Prospects of Hadoop
It must be very well noted that Hadoop framework revolutionized the field of big data processing. Though, given its challenges especially its complexity and limited ability for real time data processing that has become a key component of big data, Hadoop is facing increased competition from other frameworks like Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, that offer faster, easier, and more advanced capabilities.
However, from the fact that (1) there is increased research and development, (2) cost effectiveness since its open source and (3) an established community, the future of Hadoop is promising, as it is still widely used and adopted by many organizations. Also, there are possibilities of integrations and collaborations which will help overcome its current drawbacks such as lack of default security modules.
References
- Dean, J. and Ghemawat, S. MapReduce: simplified data processing on large clusters. Communications of the ACM, 51, 1 (2008), 107-113.
- Borthakur, D. The hadoop distributed file system: Architecture and design. Hadoop Project Website, 11, 2007 (2007), 21.
- Turkington, G., Deshpande, T. and Karanth, S. Hadoop: Data Processing and Modelling. Packt Publishing Ltd, 2016.
- Ahmed, N., Barczak, A. L. C., Susnjak, T. and Rashid, M. A. A comprehensive performance analysis of Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark for large scale data sets using HiBench. Journal of Big Data, 7, 1 (2020/12/14 2020), 110.
- Powerset, Leveraging Open Source Hadoop, Powers Microsoft's Bing - Ostatic Blog. ostatic.com.
- Shivang How does Facebook manage BigData with Apache Hadoop. scaleyourapp.com (2019).
- Suguna, S. and Devi, K. Improvement of Hadoop ecosystem and their pros and cons in Big data. International Journal of Engineering and Computer Science, 5, 5 (2016), 16680-16685.
- Jagadale, R. and Adkar, P. A Review Paper on Big data Hadoop. International Journal on Recent and Innovation Trends in Computing and Communication, 6, 5 (2018), 131-135.